|
<< Click to display Table of content >> The Buildings |
|
|
<< Click to display Table of content >> The Buildings |
  
|
The required data
The buildings in the simulation model are 3D polygons. They must have some attributes, such as number of floors, floor height and ground floor height.
The floor data is used to calculate facade maps and populations exposed in buildings (in multiple occupation).
Geometry
In MithraSIG, a building is shown in the form of a strictly horizontal 3D polygon generating a volume between the base of the building and the top of the building.
The cartographical/topographical databases produced by national geographical institutes usually offer a 2D and a 3D version of buildings:
•2D Version: the building is necessarily a horizontal polygon and usually includes attributes such as the height of the building, possibly the number of floors, the nature of the building, etc. Usually there is no absolute altimetric information and if so, the DTM must be used to position the base of the building.
•3D Version: the building can be either a 3D polygon corresponding to the digitization of roof edge or a 3D surface (Urbis 3D type). It may still include attributes such as height, number of floors, nature, etc.
Altimetric positioning
As a result of this, MithraSIG allows you to choose the altimetric positioning method that you judge to be the most reliable, depending on the available information. For example: by using the DTM to position the base of the building, then the height of the building to position the top of the building rather than the 3D polygon produced via photogrammetry, etc.
To calculate the elevation of the base of the building according to the DTM, MithraSIG allows you to choose from three options: install the building on the minimum Z, on the middle Z or on the maximum Z. MithraSIG actually calculates the Z on the DTM of each vertex on the perimeter of the building (See draping of building mode).
The precision of the data
Details of dimensions below 0.1 m should not be entered and it is better to simplify the contour. In fact, the asymptotic method used to trace the rays does not model details smaller than the length of the wave.
Display
In the software's Graphic window, buildings are represented by a colour according to their nature. When you move the cursor over a building, a tooltip allows you to see the main features of a building.
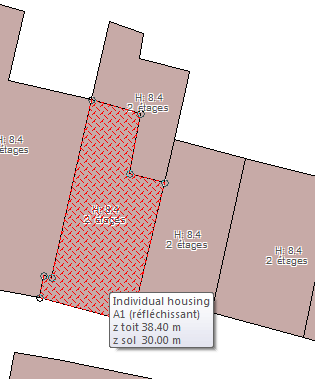
Tooltip on a building
Acoustic characteristics of buildings
Buildings are characterized by vertical and horizontal materials.
Horizontal materials correspond to foundation or roofing materials. Vertical materials correspond to facade materials.
The materials are defined in the materials database by a relative absorption index (and possibly by individual absorption indices).