|
<< Click to display Table of content >> Roads with intersections |
|
|
<< Click to display Table of content >> Roads with intersections |
  
|
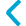
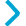
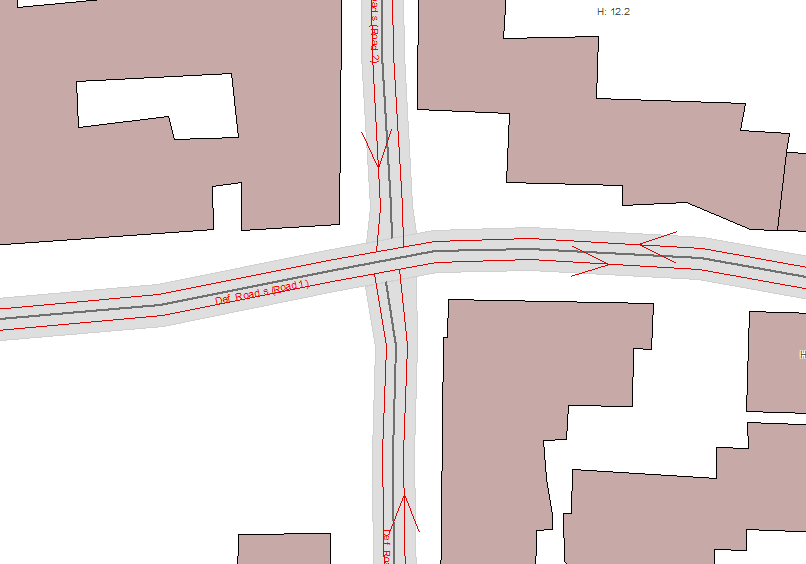
The entry of crossing roads depends on the type of intersection.
Intersection at the same level
In the case of intersections at the same level, motorway links, roads, it is necessary to initially enter the main road in the intersection then enter the other roads stopping at the side of the main road. It is necessary to avoid overlapping the lanes which cross.
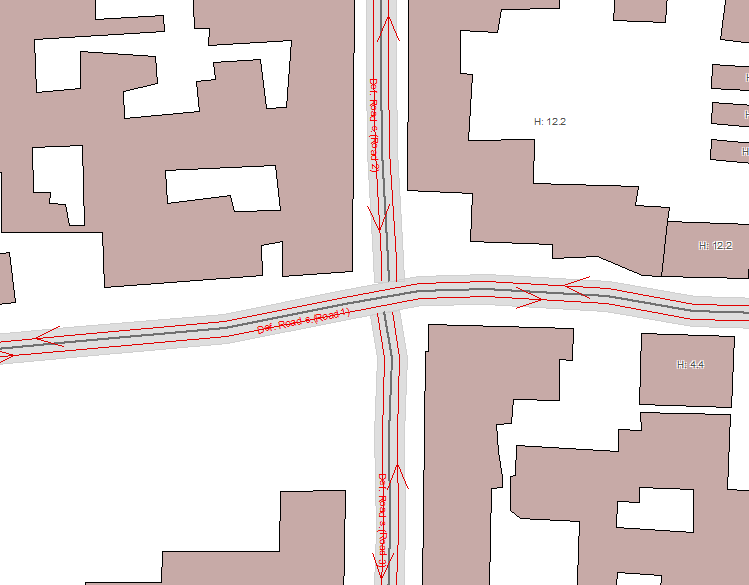 Road with intersection at the same level |
 Note: it is possible to alter each platform and each traffic geometry in order to adjust the intersection |
|---|
Viaducts and bridge structures
In this version of MithraSIG, the viaducts and bridge structures are not entered in so much as their true definitions. This option will be included in a next version of the program.
•If the superior lane has negligible traffic compared to that of the inferior lane, it is sufficient to enter the inferior lane and to stop the superior lane at the side of the road surface of the inferior lane. Nevertheless, it is important to enter the supporting walls of the viaduct.
•If the two channels cross at a right angle, it is possible to build the bridge following the principle below:
oFirst, enter the superior lane.
oThe lower lane is entered in two parts placed either side of the superior lane.
oAt the intersection, to "artificially" extend the inferior road under the viaduct, it is necessary to place part of the other of the upper road, it is said that at the two extremities of the lower road there is a reflective screen of width equal to the width of the lower road and of height equal to the height of the viaduct according to the principle shown in following Figure.
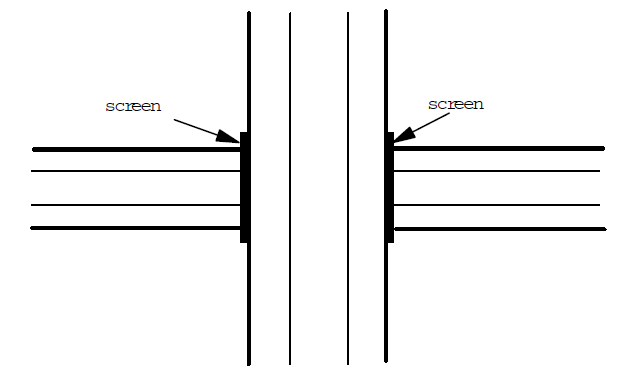 Entering a bridge in the case of two perpendicular roads |
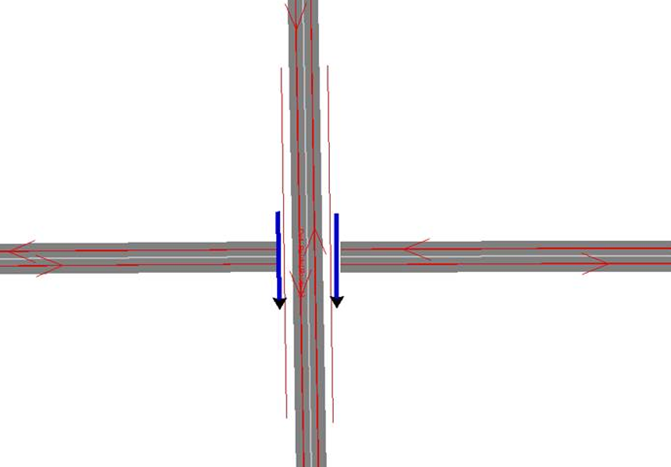 Adding a ground line above the bridge allows a better simulation of the mound creating by the bridge (platform of the road represents the top of the mound) |
|---|
•In the case where the roads cross as a flyover but are not perpendicular, it is necessary to do the calculation twice:
oThe first calculation by stopping the larger road at the side of the other road. In the case where there are vertical supporting walls under the bridge, it is necessary to represent these walls. The smaller road is left out entirely.
oThe second calculation allows the measurement of the influence of the missing part of the bridge. For this, it is sufficient to erase the smaller road and the existing parts of the other road and to enter the missing part of the part on the bridge.
In the case where the part on the viaduct has a small contribution on the group of receptors, this technique is the most appropriate because it uses a site entered with the two roads at the same time.
Another method consists in doing the calculation twice, each one for a road. As for the previous case, you must not forget to enter the supporting walls of the bridge on the site that contains the smaller road.