|
<< Click to display Table of content >> Method of population distribution |
|
|
<< Click to display Table of content >> Method of population distribution |
  
|
The simulation of population distribution only covers buildings classified as Housing (individual and collective). Other building types are ignored.
The principle is that the population of the select origin polygons is spread on intersected buildings in function of the building area. There are two ways to calculate this area and to distribute population:
•Based on the living space of each building: the number of floors is taken into account for collective housing.
•Based on the floor surface of each building: the number of floors is not taken into account for collective housing.
The distribution of population in buildings classified as Individual housing is always calculated on the basis of floor surface, whatever the method of distribution.
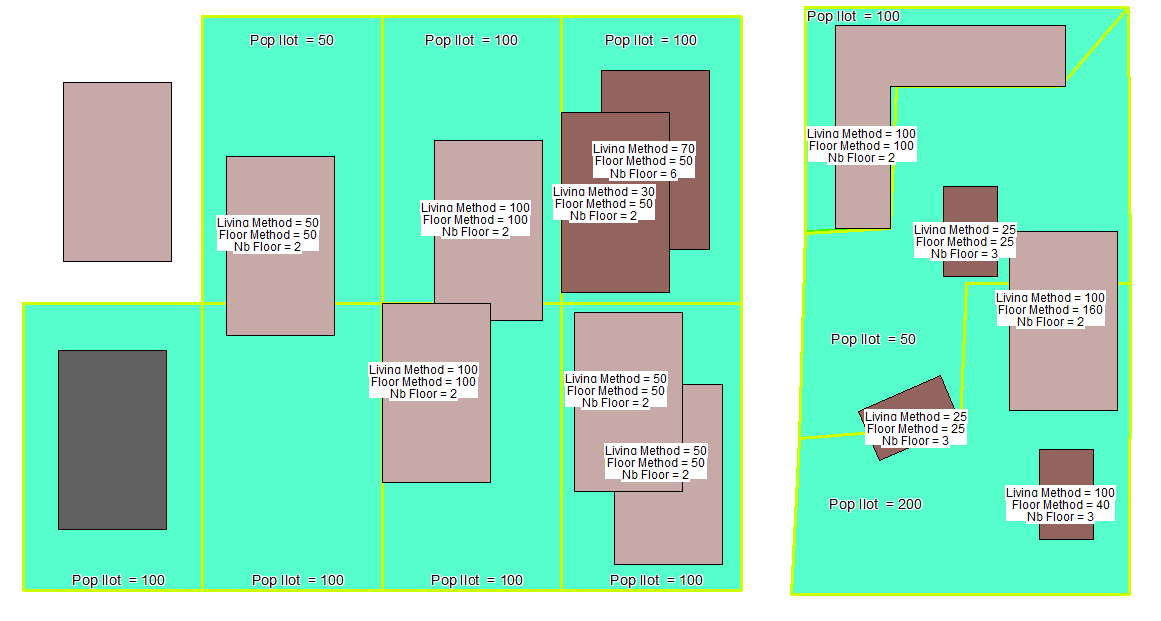
Example of population distribution
We have origin polygons of population (in blue) whose population attribute is represented by the label Pop Ilot = "100"
We have 3 types of buildings: industrial (dark gray), housing (light gray) and collective (brown).
The buildings are all the same area Sref except small one whose surface is Sp = 1/4 Sref. In the polygon with 200 inhabitants (bottom right), the small collective building Sp of 3 floors (and the ground floor) has the same population as the individual building Sref (method of distribution based on living space mode).
Population has been distributed into the buildings with the 2 methods, the results are displayed in the labels "living method" and "floor method."
•It is not possible to make successive distributions of population. For each distribution, all values for the attribute population in buildings are reset to 0.
•A building belongs to one and only one polygon: the polygon which contains its origin. If a polygon has no buildings, its population will be ignored. So:
∑(population of origin polygons) ≥ ∑(population distributed into buildings)
•The total population within the buildings is equal to the total population within the intersected polygons although there is an overlap between the origin polygons. It means that there is no geometrical tests to check the coherence between origin polygons.
•Buildings that are not of "Housing building" or are outside the origin polygons have no attribute population created.