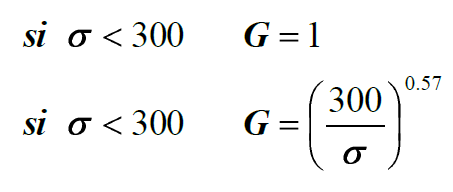|
<< Click to display Table of content >> Materials |
|
|
<< Click to display Table of content >> Materials |
  
|
The materials present in the software are represented by letters showing a gradation where A is the most absorbent and G the most reflective. This representation of materials is based on the Scandinavian Nord2000 method and builds on the work carried out in the Harmonoise and Imagine projects. The table of ground types is also that recommended by CNOSSOS-EU for strategic noise maps.
Which ground coefficient G for materials?
The French standard NF S31-133, better known as the 'NMPB method', derives the nature of the ground via an empirical parameter known as G specifying:
•G = 1 absorbent ground
•G = 0 reflective ground
The parameter G is not a physical magnitude and there is no procedure for determining its value in situ.
The physical models developed over recent years characterize ground nature by an acoustic impedance value. This value can be determined experimentally. In practice however, the impedance value is estimated by using the semi-empirical Delany and Bazley model:
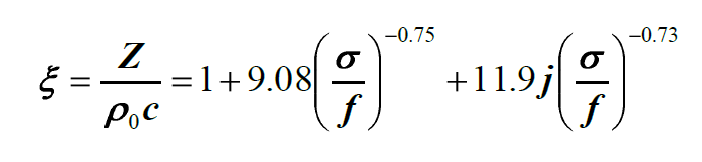
where σ is the resistance to air flow of an equivalent porous structure.
Class |
Designation |
σ (en kPa.s/m²) |
G |
A |
Very porous, snow or moss |
16.0 |
1.0 |
B |
Very porous, undergrowth |
32.0 |
1.0 |
C |
Non- compacted porous ground |
80.0 |
1.0 |
D |
Natural ground, fields or meadows |
200.0 |
1.0 |
E |
Natural ground, sand, flattened grass |
600.0 |
0.7 |
F |
Compacted ground, sand and gravel |
2000.0 |
0.3 |
G |
Mineralized ground, concrete, asphalt |
20000.0 |
0.0 |
H |
Smooth and hard surfaces, water, ice |
200000.0 |
0.0 |
In order to prepare for the integration of physical propagation models, the By- Oasis software integrates this extended classification over the binary classification of the ISO and NMPB standards.
The equivalence between the physical parameter and the parameter G input in standard simulations is given by the following empirical formula: