|
<< Click to display Table of content >> Horizontal simulation |
|
|
<< Click to display Table of content >> Horizontal simulation |
  
|
This simulation corresponds to cross sections in the horizontal plane in exterior at a define height. Buildings and roofs are taken into account for the position of the receivers. The domain of simulation is represented by a polygon.
The icon is ![]() .
.
Settings
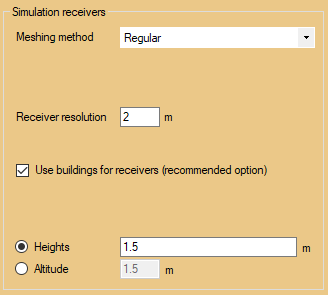
Horizontal simulation
•Receiver resolution: distance between receivers.
•Height: height at which the map will be made. A simulation with a constant height follows the relief. It is possible to simulate at several heights in one time. For this, enter heights separated by a ";".
•Altitude: altitude at which the map will be made.
•Use buildings for points: Building are used as a break line of the meshing triangulation. For each vertex of the buildings, a receiver is created (and along the facade) with an offset of 10 cm. The option is used for results accuracy and to compute max level in building (map).
•Meshing method: (Regular/Irregular/Progressive).
oRegular meshing: Regular positioning of receivers over the entire simulation area. The receivers are not positioned inside buildings.
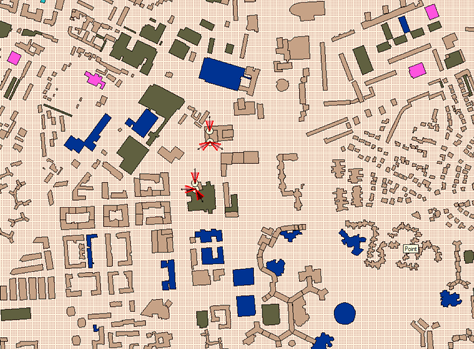
Regular meshing
oIrregular meshing: Positioning of receivers with greater density in zones close to the antennas. This makes it possible to run simulations much faster in zones where the level is lower. The Irregular method makes it possible to specify a second resolution, Receiver rez 2, which is applied beyond a distance from the antennas (Mini dist.transmitt.).
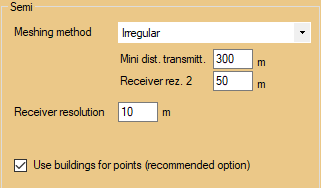
Irregular meshing
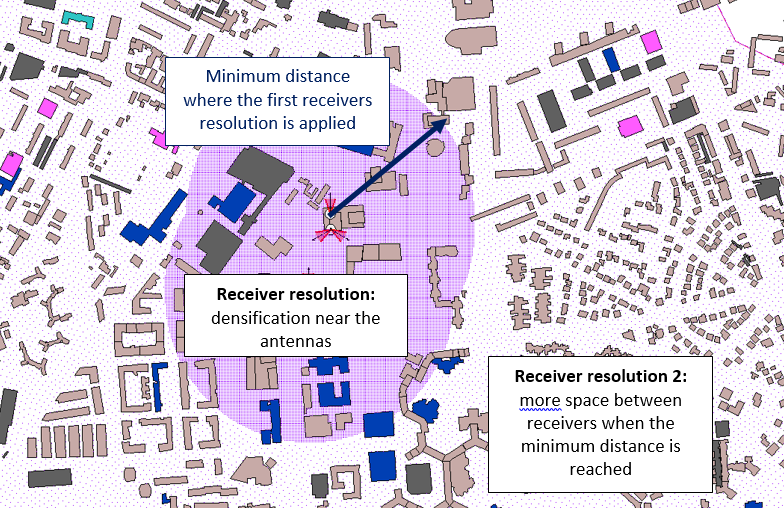
Irregular meshing
oProgressive meshing: Distance between receivers decreases from the antenna over the entire simulation area. Coefficient is the coefficient to decrease the density of receivers (function of distance) in the meshing. We recommend values between 1.05 and 1.001. The receivers are not positioned inside buildings.
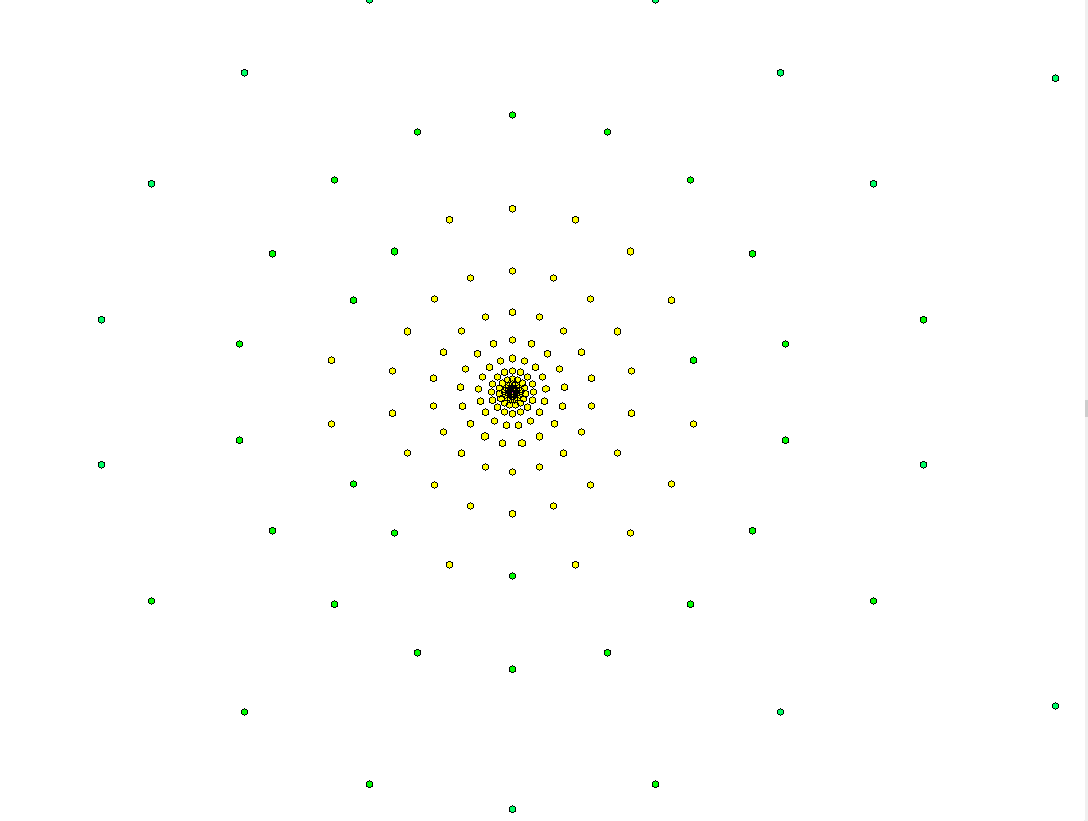
Progressive meshing
Let’s see an example of some progressive coefficients on horizontal domain. If the coefficient increases a little bit, the number of receivers and therefore the calculation time decrease a lot.
Coefficient |
Number of receivers |
Computation Time |
1 |
1 337 283 |
10 m 47 s |
1.05 |
6 961 |
1m 05 s |
1.01 |
73 184 |
1m 20 s |
1.005 |
173 038 |
1m 53 s |
1.001 |
675 746 |
5m 08 s |
1.1 |
2 340 |
1m 05 s |
Advise: Use regular meshing in urban areas, irregular meshing in large rural areas, and progressive meshing in huge domains.
|
Horizontal simulations take into account the roofs for the positioning of the receivers. 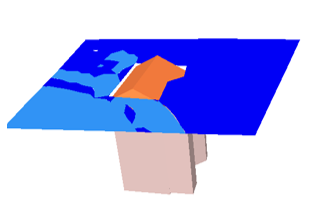 Horizontal simulations with roofs |
|---|