|
<< Click to display Table of content >> Rendering |
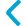  
|
|
<< Click to display Table of content >> Rendering |
  
|
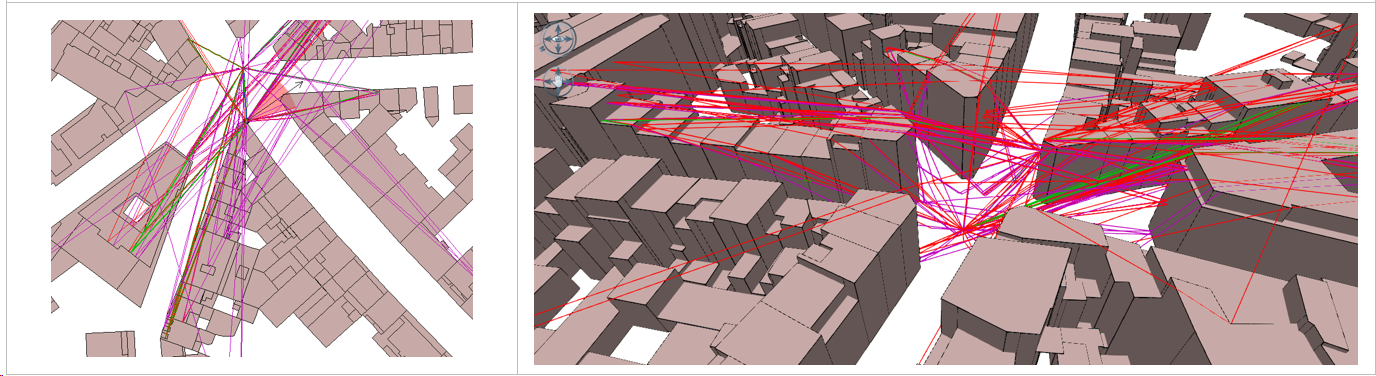
Example of a ray for a 3-reflection calculation
Clicking on a ray displays its properties in a specific control. The information available is :
•Receiver name its ID and height
•Antenna (No and Name to which the beam belongs)
•Number of reflections and diffractions of the beam
•Geometric cross-section of the beam
•E-field associated with the beam
•Min and Max calculation frequencies for this beam
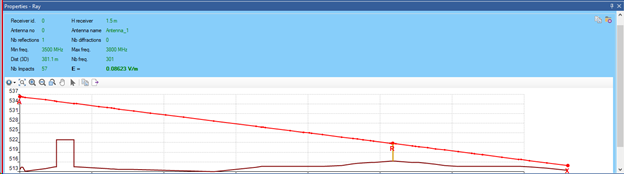
User Interface of ray section
The E field corresponds to the root mean square of the |E| for all calculation frequencies. If there's only one direct path, this field corresponds to the final E of the receiver. Otherwise, ray summation depends on interference.
If several rays are selected, nothing is done.
Description of impact values indicated by letters:
•G = ground reflection at receiver position (= receiver attached to ground/roof, reflection just before reaching receiver)
•S = ground reflection
•F = reflection from facade at receiver position (= receiver attached to facade, reflection just before reaching receiver)
•R = reflection from facade / vertical wall
•H = horizontal diffraction
•V = vertical diffraction
•A = Antenna
•X = Receiver
Export Ray
Rays can be exported directly in KMZ format for visualisation in Google Earth. Before export, the rays will be clamped to ground in order to obtain an altitude consistent with the Google Earth model.
Instead of storing x, y, z, we'll store x, y, h, where h is the height.
To do this, before exporting, we'll apply the following formula to each ray vertex:
H export = Z ray – Z ground
