|
<< Click to display Table of content >> 3D view |
|
|
<< Click to display Table of content >> 3D view |
  
|
The 3D view of MithraSIG can be activated by clicking on the button ![]() in the tab Simu - Renderings.
in the tab Simu - Renderings.
Items cannot be edited in the 3D view, but can be selected to read their properties.
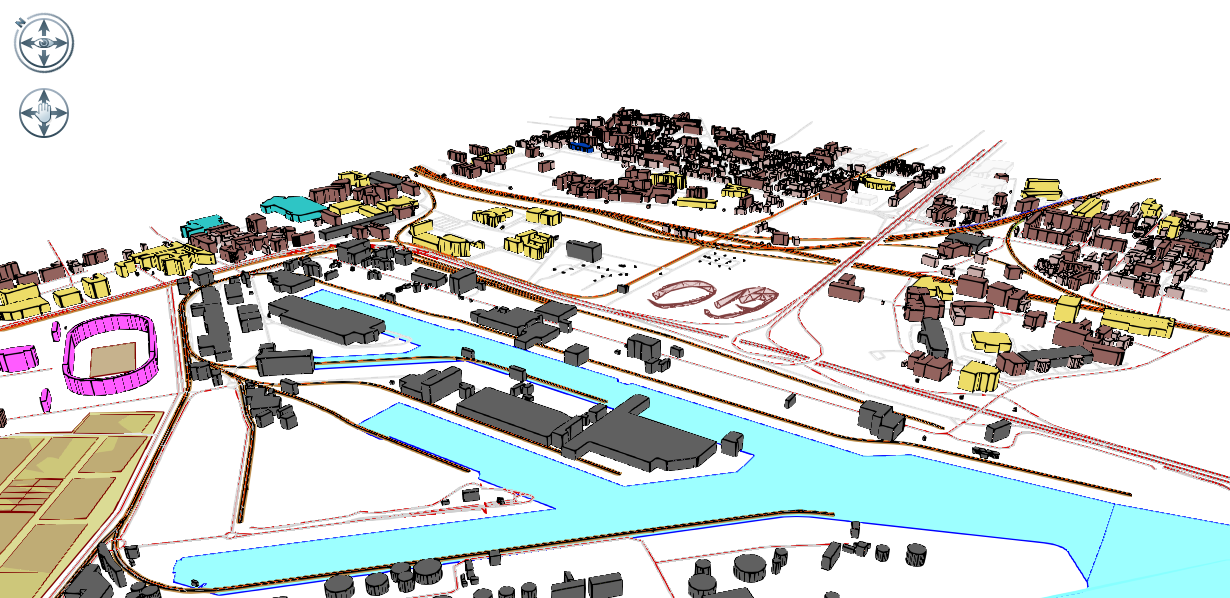
3D view
Depending of the performance of the machine, the initialisation of the 3D view can be slow. We recommend to hide some overlays that can be heavy to handle before opening the 3D view, and display them after.
The overlays that could reduce 3D performances are:
•DTM.
•Ground, if this one has a lot of Points items.
•Maps of type Points, because of the large number of receivers that can contain be displayed.
•All other overlay from Input Data containing a large number of items.
Navigation
Several mods are available for the navigation in the 3D view.
•Zoom in/Zoom out
oWith the mouse wheel.
oWith the keys + and * of the keyboard.
•Rotate the view
oWith the mouse wheel button that rotates the view relative to the center of the view, turn around the model. This center is the one of a 3D cube corresponding to the extent of the itmes in X, Y and Z.
oWith the button Look  that do a rotation from the point of view, turn the head. Place the cursorPlacer le curseur de la souris sur le bouton Regard et maintenir le bouton gauche de la souris et bouger le curseur pour s'orienter.
that do a rotation from the point of view, turn the head. Place the cursorPlacer le curseur de la souris sur le bouton Regard et maintenir le bouton gauche de la souris et bouger le curseur pour s'orienter.
•Move
oWith the left button of the mouse that move the view.
oWith the button Move  that move the view.
that move the view.
3D Options

3D view options
•Reset: reset the orientation of the 3D view.
•Exaggerate heights: set a factor to increase the heights of the items (can be useful when the project is "flat").
•Wireline: display only the edges of the items.
•3D Properties: see below.
3D Properties
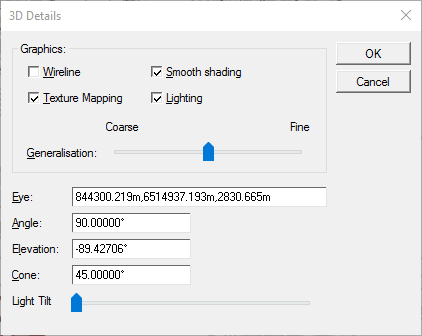
3D Properties
•Wireline: display only the edges of the items.
•Smooth shading: Surface items will be "smoothed".
•Texture mapping: display/hide textures, e.g. draped bitmaps.
•Lighting: turn on/off lights in the view.
•Generalisation: generalise the vertices of the items according to a factor, allowing a lighter rendering for the manipulation in the 3D view.
•Eye: the eye position, i.e. where to look from.
•Angle: the viewing angle, about the vertical (Z) axis.
•Elevation: the viewing elevation, above or below the XY plane.
•Cone: the perspective viewing angle.
•Light tilt: the slider controls the tilt of the 3D light.